Leetcode 0094. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values. Example 1: Input: root = [1,null,2,3], Output: [1,3,2] Example 2: Input: root = [], Output: []
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example 1:
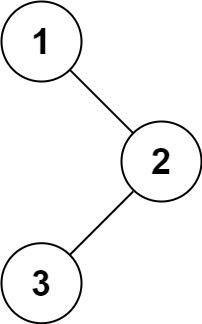
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up
- Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* Recursion
* Time Complexity: BigO(n)
* Space Complexity: BigO(n)
*/
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, nums);
return nums;
}
/**
* Depth First Traversal: Inorder
* Left -> Node -> Right
*/
private void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, nums);
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.